Inbound Logistics vs. Outbound Logistics
Return To List
Return To List
Logistics refers to the secure transfer of raw resources and completed commodities. According to a Statistic investigation, certain states spend more money on logistics, transporting goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption via various supply chain network segments. Without excellent logistics, a firm cannot compete for profits.
What is logistics?
Even though the terms logistics and supply chain are sometimes used interchangeably, logistics is a component of the overall supply chain. The transfer of commodities from point A to point B is referred to as logistics, which involves two functions: transportation and warehousing. The complete supply chain is a network of companies and organizations that collaborate to create and distribute goods through various activities such as logistics.
What is logistics management?
Logistics refers to the set of procedures involved in transporting goods internally or from buyer to seller. Logistics managers supervise and handle the process's various intricacies. These persons can get a variety of certifications, and many aspects must be considered to be successful. Routes must be determined based on practicality, legal requirements, and avoiding obstructions such as road maintenance, wars, and bad weather. When selecting a transportation provider and packaging method, costs must be balanced against weight and recyclability.
Fortunately, logistics management software can help firms make the best routing and shipping decisions while also controlling costs, protecting investments, and tracking item movement. Such software can frequently automate processes such as selecting shippers based on rate fluctuations or contracts, printing shipping labels, automatically entering transactions in ledgers and on the balance sheet, ordering shipper pickups, recording receipts and receipt signatures, and assisting with inventory control, among other things.
What Is the Distinction Between Inbound Logistics and Outbound Logistics?
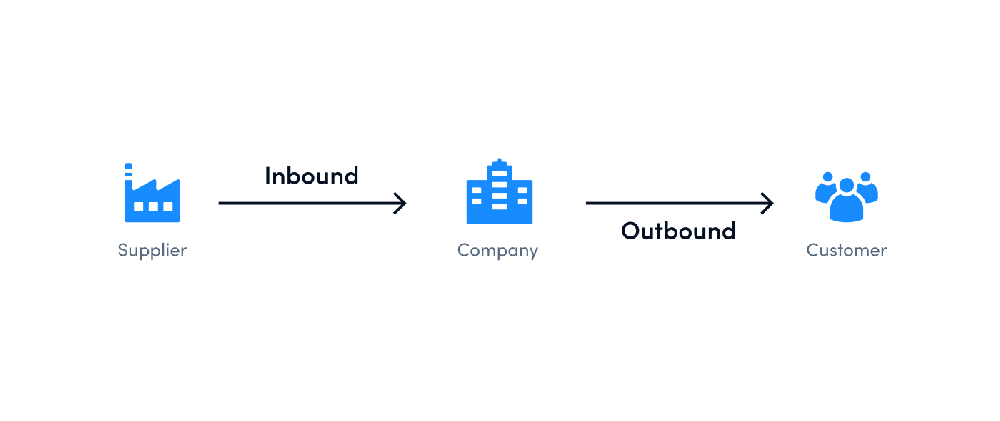
Inbound logistics includes bringing supplies or resources into a firm, and outbound logistics involves delivering goods and products to clients. Both are highly focused on the transportation of commodities. On the other hand, inbound is all about receiving, while outbound is all about delivering.
Inbound Logistics:
Inbound logistics is the way materials and other goods are brought into a company. This process includes the steps to order, receive, store, transport and manage incoming supplies. Inbound logistics focuses on the supply part of the supply-demand equation.
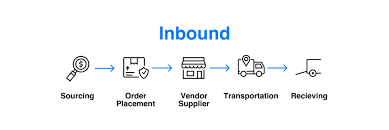
Challenges of Inbound Logistics
Inbound logistics is a form of logistics within a company’s supply chain. While these are common practices in the industry, they are fairly complex as they involve many different parties.
High costs, unknown delivery dates, and unexpected lead times are the key issues of inbound logistics. This makes it difficult for firms to maintain optimal inventory levels while also improving warehouse efficiency and productivity.
Outbound Logistics:
Outbound logistics refers to moving goods from a manufacturer to a retailer and vice versa. The product is made at the manufacturer, then a company will either store or sell it. This process occurs in a warehouse or distribution center, which must be close to the retail location. Outbound logistics is concerned with the supply side of the supply-demand relationship. The procedure includes storing and transporting items to the client or end user. Among the phases are order fulfillment, packaging, shipping, delivery, and customer assistance connected to delivery.
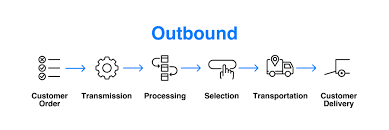
Challenges of Outbound Logistics
Outbound logistics challenges can hurt profits and customer satisfaction. Inventory and shipping costs can rise quickly, while incorrect or late orders will drive customers away. This process's challenges include managing inventory, transportation costs, and labor.




